Hackers study their targets and learn how to circumvent their defenses in order to obtain what they want. This applies to cyberattacks against both individuals and companies.
If they study companies so they can attack them, business owners and professionals responsible for company data security should also study how to protect themselves.
The motives for the attack, in turn, can be varied, such as obtaining confidential and sensitive information or stealing as much money as possible from the company.
According to an analysis by Kaspersky, extortion and Bitcoin theft will increase in 2021 , with financial cyber threats being among the most dangerous, as they directly imply losses for victims. It is inevitable that the changes (adoption of home office due to the pandemic) that occurred in 2020 have influenced the modus operandi of cybercriminals.
In this article, you will see why companies are frequent targets of cyberattacks, and what the most common attacks are.
Why do hackers target companies?

As I wrote earlier, cybercriminals study their targets to obtain as much information as possible, facilitating persuasion and identifying potential security breaches in companies' internet networks.
Much of the information about the company and its employees, used to orchestrate the plan, is freely and easily available on social media, such as workplace, name, date of birth, preferences, and habits. Speaking of which, social media and cloud services are targets for hackers. Another survey reveals that Facebook, WhatsApp, Amazon, Apple, and Netflix were the five most used brands in phishing attacks in 2020, as you can see in the table below:
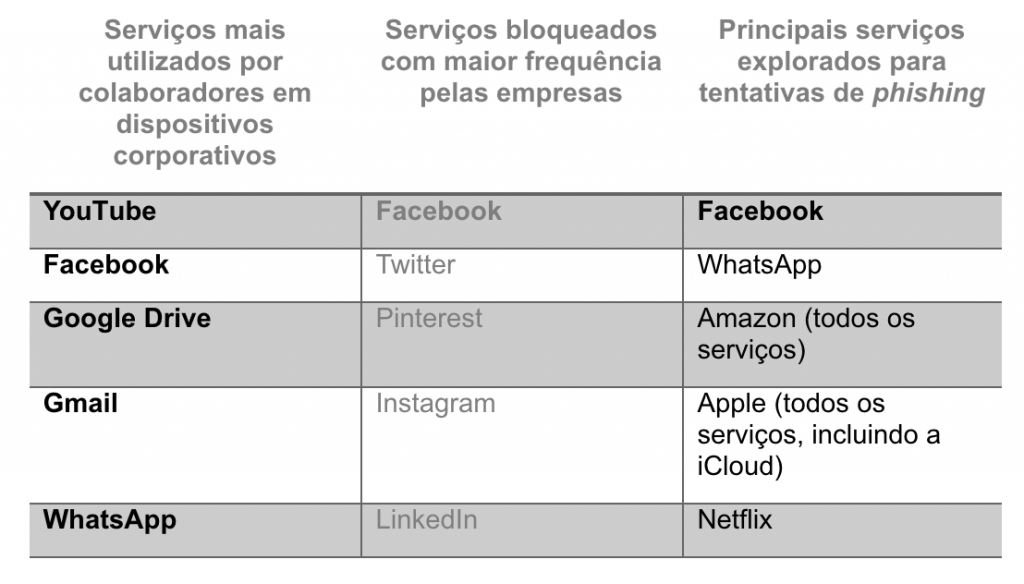
After learning about your employees, the hacker can send an email with a link or attachment, for example, that installs software and gives the attacker control of the device. This email can be personalized with the user's real information, making it more attractive to click.
However, the main factor that makes companies a constant target of attacks is financial. With minor exceptions, virtually all companies conduct banking transactions and use internet-connected systems for bill payments and transfers. With this fact in mind, cybercriminals resort to attack techniques such as falsifying invoices from potential suppliers or even simulating a financial institution's website to collect banking data. Furthermore, in attacks involving data kidnapping, companies that lack data backup systems are held hostage, forced to pay high sums to criminals in exchange for the return of their data.
Next, we will look at the main types of attacks suffered by companies and some characteristics of each one.
What are the main cyberattacks on companies?
Information security has been increasingly promoted as a contingency strategy, especially in a year when the situation became very favorable for cybercriminals with the rise of remote work.
If you, as a manager, business owner, or IT professional, want to keep your company protected against cyberattacks, the first step is to understand how they work and what the main types of attacks are today.
In the following lines, we cite some of the main cyberattacks on companies and some variations that have been improved in recent months.
DDoS Attack
The main objective of this attack, which translates to "Service-Assigned Browsing," is to overload server activities, causing system slowdowns and making websites and access unavailable.
Since many professionals are more connected due to social isolation, this type of attack, if well-distributed, can go unnoticed by security. A DDoS attack is one of the biggest threats to the full operation of a company's systems.
In February 2020, the company Bitfinex suffered a DDoS attack and needed to perform urgent maintenance to investigate the attack .
Port Scanning Attack
If there is any vulnerability in the company's system, this malware searches the server in an attempt to find it. If it manages to find the security breach on the company's server, it steals information and data in order to damage the system or hijack the data.
The SempreUpdate portal has published a study on the 3 ports that should not be opened on the company's router .
Ransomware
Widely known as "data kidnapping," ransomware blocks access to all files on the attacked server, and they are only released after payment of a sum of money (usually bitcoins), with the amount of the "ransom" determined by the kidnapper.
A good example of a ransomware attack was the recent attack on Honda Motor, which suspended part of its production, including in Brazil .
Trojan Horse
Popular on the internet, this malware only works with the user's "permission." Simply put, the individual executes an email attachment from a suspicious or unknown sender, or performs a suspicious download containing the camouflaged virus.
There are numerous objectives in a Trojan horse attack. Among them are stealing personal information and disrupting computer functions.
Brute force attacks
Imagine that to open a padlock with a numerical code, you would have to try all possible combinations. Sounds time-consuming, right? But in the digital world, this can be done very quickly. A brute-force attack steals accounts through numerous attempts at username and password combinations in a very short time.
With this information, the criminal can send numerous messages from sender known to the user, containing content such as phishing and spam, requesting deposits, transfers, access passwords, and many other sensitive details.
According to Kaspersky, a leading company in security software, the number of brute-force attacks on businesses has increased by 333% in two months .
Phishing
Phishing, usually carried out via email, is a cyberattack in which hackers trick users into revealing confidential information, including passwords, bank details, and social security numbers.
The attack is usually well-constructed and leads the user to a page identical to the real page, such as that of a bank branch.
As the name suggests, hackers "fish" for user data, throwing out "bait" to trick them.
It is one of the most common and successful types of attacks, and there are numerous news reports about this attack spread across the internet.
Employees are the gateway for cyberattacks

There are countless entry points for a cyberattack. Emails, malicious files, fake links, fake advertisements, among many others. Internet security systems such as firewalls, antivirus software, and backup systems can add an extra layer of security to the internet in a business environment. However, the key point for attacks within companies is the users.
Lack of knowledge, carelessness, or the infamous "I know what I'm doing" attitude make employees the biggest security vulnerability for companies on the internet. Therefore, training employees and maintaining an internet security policy within the company is just as important as security systems.
But it's not all roses. You can probably imagine that relying on the knowledge and common sense of employees doesn't seem like a very good idea.
According to a Tessian survey, two-thirds of employees are not regularly trained on cyber threats . And most of those who are trained don't remember what they were taught.
As mentioned earlier, hackers study their targets and prepare attacks that, for unprepared and untrained employees, are easy targets.
Unfortunately, there is still no single solution capable of solving all internet security problems for businesses at once. However, there are several effective ways to close the vast majority of entry points for cyberattacks against companies on the internet.
In the Internet Security Guide for Businesses, you will find a list of best practices for internet security , so you can protect yourself against cyberattacks.
Until later!










2 comments
Comments closed