Corporate cybersecurity has ceased to be merely a technical issue and has become a key component of the business. By 2026, companies that know how to protect their data, manage identities, and use artificial intelligence intelligently will gain resilience, operate more efficiently, and earn the trust of customers and partners .
In this article, you will find the 5 trends that are changing the game in cybersecurity , data from Brazil and the world, and practical tips to transform threats into growth opportunities.
The threat landscape that defines 2026
Corporate security is changing rapidly. The old concept of "network perimeter" has evolved. Today we have a distributed environment, where identities, cloud apps, and digital supply chains create new challenges (and opportunities).
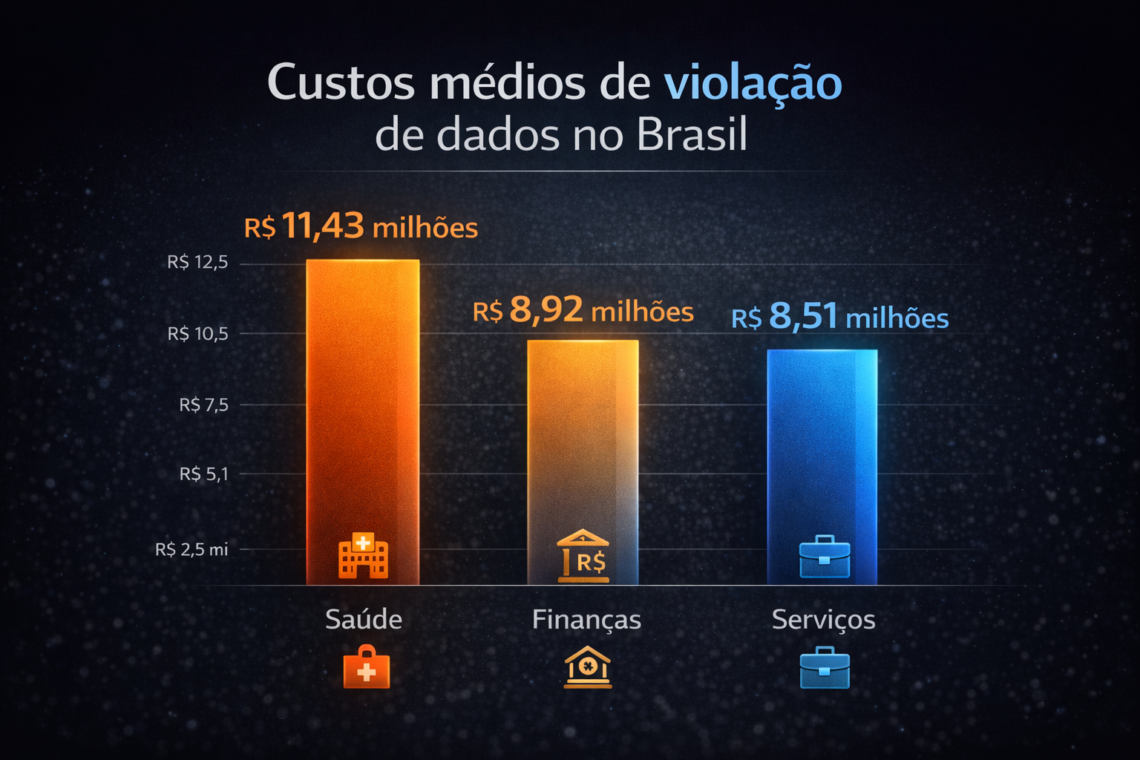
In Brazil, the sectors that suffer the most from violations are:
- Health: R$ 11.43 million
- Finances: R$ 8.92 million
- Services: R$ 8.51 million
Companies that adopt modern security not only reduce risks, they also gain agility and market confidence .
Key changes since 2025
The past year has accelerated trends that were already gaining momentum. Hybrid work has become established in many companies, and this has reinforced the need for security models that work from anywhere. The integration between systems through APIs has created more agile environments, but also more connected (and more vulnerable).
Artificial intelligence is no longer something out of a futuristic movie; it has become an everyday tool for both its proponents and its opponents. It's an innovation race on both sides.
Privacy regulations have also matured considerably, establishing clearer standards. Compliance is no longer just an obligation; it has become an opportunity to stand out. Companies that demonstrate maturity in security gain real advantages in negotiations and partnerships.
1. Digital extortion without encryption: rethinking data protection
Ransomware is evolving in a way that demands smarter responses. For years, the main tactic was to encrypt everything and demand a ransom. Today, specialized groups are changing their strategy: they steal your data silently and threaten to release everything .
This teaches us something important: having robust backups is essential, but it doesn't solve everything. In 2026, effective protection means having deep visibility into sensitive data, well-tuned access controls, and the ability to detect unusual activity before critical information leaves the company.
How do the new attacks work and what does this mean?
Modern attacks prioritize going undetected. Attackers gain entry through stolen passwords (the most common vector according to the Verizon 2025 report ) and remain there quietly for weeks or months. During this time, they map the environment and steal the most valuable data little by little.
But here's an opportunity: the longer an attacker needs to stay in your environment, the more chances you have of catching them . Organizations that invest in continuous monitoring are turning this window of time into an advantage.
Protection strategies that work
An effective response involves several layers. First, classify your sensitive data to know where to focus your efforts. Then, use modern Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools integrated with behavioral analytics. They can identify theft attempts even when they are made gradually.
DNS layer protection complements these strategies by acting on the communication channel, filtering name resolution requests, blocking malicious domains, and hindering connections to phishing sites and command and control infrastructures.
Network segmentation also helps a lot if an attacker gets in; they can't freely roam everywhere. And strict privilege management creates multiple points of resistance.
IBM Cost of a Data Breach 2025 report shows the impact: Brazilian companies with good detection capabilities reduce costs and accelerate recovery. Implementing threat intelligence saves an average of R$ 655,110 , and using AI governance technologies saves R$ 629,850 . Investing in detection pays off.
2. Identity Management as a Strategic Foundation
Identity has become the new security perimeter. With distributed work, cloud-based apps, and hybrid systems, each person's or system's credential is an access point that needs to be well managed.
The opportunity presented by non-human identities
Here's a surprising fact: your company today has far more "digital users" than people. We're talking about APIs, automated services, bots, and IoT devices—everything that requires credentials to access systems and data.
To give you an idea: in some organizations, there are 144 of these automatic identities for each person . And that number grows by 44% per year.
Why? The more you automate processes, the more "machine accounts" you create. And there lies the challenge: these identities need the same level of management and security that human accounts receive .
Companies that do this well gain not only security, but efficiency. Passwords are changed automatically, access is adjusted according to actual needs, and there is complete visibility of everything that is happening.
Passwords as a leverage point
The Verizon 2025 report confirms: stolen passwords are the most common entry point. But this points to a clear solution: strengthening authentication offers one of the best returns in security.
Multifactor authentication (MFA), especially on accounts with high privileges, greatly reduces risk. Modern solutions are increasingly transparent to legitimate users, while blocking suspicious attempts.
Behavioral analysis allows you to detect when valid passwords are being used in unusual ways: access from different locations, unusual times, patterns that don't match the history. This transforms password weaknesses into a source of intelligence.
Zero Trust: evolution, not revolution
The Zero Trust model is essentially the natural evolution of security. Instead of automatically trusting everything "inside the company," every access is continuously validated.
Implementing Zero Trust doesn't mean throwing everything away and starting from scratch. Companies that do it well adopt a gradual approach: they start with critical areas, prove it works, refine it, and then expand.
The benefit goes beyond security. Well-designed Zero Trust environments typically offer a better experience for legitimate users, with smarter validations and less unnecessary friction.
3. Advanced observability: from reactive to proactive
The shift from traditional monitoring to advanced observability is one of the most important transformations in security. It's not just about detecting known problems, but about deeply understanding the environment to identify subtle signs of compromise.
Beyond the alerts: contextual understanding
Traditional SIEM systems have their place, but they primarily function by reacting to known events. Advanced observability goes further, with behavioral analysis that learns what is "normal" for each part of the environment.
Machine learning identifies patterns that are impossible to codify into rules: typical traffic volumes, usual sequences of actions, relationships between systems, standard schedules. Deviations from these baselines, especially when they appear together, signal situations that deserve attention.
This ability to put things into context greatly reduces false positives. Instead of overwhelming the team with thousands of alerts, intelligent systems prioritize what really matters.
Early detection as a competitive advantage
The IBM 2025 report shows that companies take an average of 241 days to identify and contain a breach, the shortest time in nine years, but still a long time. In Brazil, companies that use AI and automation face average costs of R$ 6.48 million per breach, while those that do not see costs rise to R$ 8.78 million . A difference of 26%.
Every day an attacker operates undetected increases the damage. Early detection not only reduces damage, but also allows for a more targeted response, minimizes disruptions, and preserves more evidence for investigation.
Leading observability companies report an added benefit: a better understanding of their own infrastructure. The deep visibility needed for security also illuminates optimization opportunities.
Building responsiveness
Detection is key, but a good response is what makes the difference. Automated response to known threats allows for containment in seconds: isolating compromised machines, canceling suspicious passwords, and blocking malicious communications.
For situations that require human judgment, having rich context accelerates decisions. Analysts receive not just an alert, but a complete story: which systems were accessed, which data was touched, what the sequence was, and what other identities may be compromised.
This combination of automation for the obvious and human intelligence for the complex creates the perfect balance between speed and precision.
4. DNS Protection: The Invisible First Line of Defense
DNS is present in all communication on your network , and that's precisely why it has become a strategic point of security.
By 2026, DNS layer protection will no longer be "just another tool" but will become the foundation of any modern security strategy . Why? Because it acts at the exact moment your systems attempt to connect with the outside world.
Why is DNS so important for security?
Every time a device on your network attempts to access anything external, whether it's an employee opening a website or malware trying to communicate with your command server, a DNS lookup occurs first. This makes DNS a privileged point of contact for observing and blocking threats.
Think of it this way: if an attacker manages to compromise a machine on your network, they'll need to communicate with their external infrastructure. This could be to receive commands, send stolen data, or download other tools. And to do all of that, they need to resolve domain names. That's where DNS protection comes in.

What DNS protection actually blocks
- Phishing and malicious websites: When an employee clicks on a suspicious link in an email, the DNS protection identifies that domain as known for phishing and blocks access. The user doesn't even get to see the fake page.
- Malware communication: Ransomware and other malware need to "call home" to communicate with command and control servers. DNS protection maintains constantly updated lists of known malicious domains and blocks these communication attempts, halting the attacker's operation.
- Access to compromised websites: Even legitimate websites can be hacked and used to distribute malware. Real-time threat intelligence identifies when a known domain has been compromised and blocks access until the issue is resolved.
Why is DNS so effective?
The great advantage of DNS protection is that it works for the entire network, all the time, on all devices .
- It doesn't depend on installed software: it works for computers, cell phones, tablets, IoT devices, printers, anything connected.
- Works 24/7: protects devices inside and outside the office, including during remote work.
- Act quickly: Block threats at the time of the DNS query.
- It offers complete visibility: you see all external connection attempts on your network, creating intelligence about behaviors and patterns.
How DNS integrates with other security layers
DNS protection doesn't replace other tools; it complements and enhances them. When integrated with SIEM, firewalls, and detection systems, it creates an extra layer of intelligence
- Detection of compromised devices: A computer making hundreds of strange DNS queries may indicate an infection.
- Attack mapping: DNS logs help to understand what the attacker did and to reconstruct the timeline.
- Richer context: Combining DNS data with other sources greatly facilitates the investigation.
Solutions like Lumiun DNS , for example, offer this protection in an integrated and intelligent way, blocking known threats and detecting suspicious behavior in real time.
The Verizon 2025 report shows that stolen credentials are the most common initial vector, but the attacker's journey always includes external communication, and that's where the opportunity to disrupt the attack through DNS lies.
Practical implementation by company size
Small businesses: starting with DNS protection is one of the best decisions. You get robust security with an affordable investment and almost zero maintenance. Set it up once and it protects everything automatically.
Medium-sized businesses: In addition to basic blocking, use DNS behavior analysis to catch anomalies. Integrate DNS logs with your SIEM to connect the dots. Use different policies by department or user type.
Large organizations: advanced DNS protection with machine learning to catch unknown threats, deep pattern analysis, full integration with your security stack, and threat intelligence tailored to your company's risk profile.
5. AI in security: amplifying human capabilities
Artificial intelligence is transforming cybersecurity in practical and measurable ways. The question is no longer whether to adopt AI, but how to do so in a way that amplifies human judgment without creating blind dependence or new risks.
AI as a defense accelerator
Machine learning allows for the analysis of data volumes that are impossible to process manually. Models trained on terabytes of network data and system behavior identify subtle patterns that indicate compromise before significant damage occurs.
Companies that have implemented behavioral analytics with AI report earlier detection and a dramatic reduction in false positives. Systems learn what is normal for each user, application, and data flow, flagging deviations that warrant human attention.
The IBM 2025 report documents that Brazilian companies with extensive use of AI and automation face 26% lower breach costs: R$ 6.48 million compared to R$ 8.78 million in organizations without these technologies. These are not theoretical benefits; they are real results measured in the Brazilian market.
Automated response with human supervision
Automation enables rapid response. Containment of known threats happens in seconds: isolating machines, canceling passwords, blocking malicious communications. This frees analysts to focus on in-depth investigation and strategic decisions.
The key lies in proper calibration. Automated systems should be reliable for low-risk, high-value actions: blocking known malicious IPs, disabling clearly compromised accounts. Decisions with greater operational impact still require human validation.
This division creates synergy: machine speed combined with human wisdom. Analysts receive rich context, and automation handles repetitive tasks, allowing expertise to be applied where it truly matters.
AI governance as an opportunity
The increasing use of generative AI in companies creates a need for clear governance. Research shows that 63% of organizations still lack adequate policies for AI use . This gap represents an opportunity: companies that establish structured governance reap the benefits of innovation while maintaining control over risks.
Effective governance doesn't mean prohibiting use; it means guiding adoption with clear guidelines on appropriate cases, protection of sensitive data, and responsibilities. Companies that do this well find that clear policies accelerate safe adoption, rather than limiting it.
How can your company evolve in 2026?
Transforming knowledge into real progress requires a structured approach. The most successful companies treat safety as a continuous journey of improvement, not a project with a deadline.
Prioritizing by maturity and context
The security approach needs to be proportionate to the stage and resources of each company. There is no single recipe; what works for a multinational corporation may paralyze a small business, while basic solutions leave large organizations exposed.
For small businesses , the path begins with well-executed fundamentals:
- Universal multifactor authentication
- Automated and regularly tested backups
- Agile processes for updating critical systems
- Culture of safety awareness
- DNS protection (see trend 4) — a first line of defense with excellent cost-benefit
When specialized capabilities become necessary but impractical to maintain internally, managed security services offer access to 24/7 monitoring without the costs of a dedicated team.
As companies grow , medium-sized businesses face new challenges:
- Structured management of identities (human and non-human)
- Intelligent network segmentation
- Internal incident response capability
- Supplier evaluation processes
- DNS protection with behavioral analysis and SIEM integration
Large organizations , having consolidated these capabilities, face orchestration challenges:
- Progressive implementation of Zero Trust
- Advanced observability integrating multiple sources
- Robust third-party risk management programs
- 24/7 security operations with active threat intelligence
- Advanced DNS protection with machine learning and zero-day threat detection.
Balancing technology and people
Tools amplify human capabilities, they don't replace them. Investing proportionally in technology and people development creates synergy where each element enhances the other.
- Technical training keeps expertise up-to-date.
- Awareness programs transform people into an additional line of defense.
- Leadership that understands safety as a strategic issue ensures adequate support.
Metrics that drive progress
Effective KPIs measure results, not just activities:
- Mean Time To Detection (MTTD) and Mean Time To Containment (MTTC) show how quickly you identify and respond to incidents.
- Percentage of assets with full monitoring coverage.
- Visibility of identities (human and non-human).
- MFA adoption rate , especially in privileged accounts.
- Percentage of critical suppliers undergoing continuous evaluation.
- Correct identification rate in phishing simulations.
Security as a business enabler
Cybersecurity has evolved from a technical function to a strategic driver. Customers choose vendors that protect data. Partners value integrations with companies that take security seriously. Investors consider security maturity when assessing risks.
The trends discussed in this article—the evolution of extortion attacks, the centrality of identity management, the power of advanced observability, DNS protection as a first line of defense, and the potential of AI—represent not only challenges but also opportunities for differentiation .
Companies that invest in proactive security build not only protection against threats, but also capabilities that support innovation and growth.
In 2026, leadership in security is leadership in business. The question is not whether your company will face security challenges, but how prepared it will be to transform them into opportunities to strengthen operations, build trust, and accelerate strategic objectives.









