Did you know that believing certain myths about digital security can be costly for your company? Find out what they are and protect yourself before it's too late!
Digital security is essential for companies of all sizes. However, many businesses underestimate cyber risks , believing myths that put data and operations at risk. With increasingly sophisticated attacks , adopting effective protective measures becomes essential.
Even with investments in basic security, many companies feel overly secure. The problem is that hackers exploit any breach , and relying on outdated practices can be disastrous.
Cyberattacks have skyrocketed in recent years, affecting organizations of all sizes. According to data from Check Point Research , there was a 30% increase in cyberattacks in the second quarter of 2024 compared to the same period in 2023, reaching an average of 1,636 attacks per organization per week.
In this article, we'll dispel seven myths about digital security that expose your company to risks. We'll also present strategies to strengthen your protection and avoid financial losses and data loss .
Myth 1: “My company is small, no one will want to attack it”
Small business owners believe that hackers only attack large corporations , but that's not true . According to a Verizon report , small businesses face 47% of attacks , while large organizations account for 55% . This proves that company size doesn't matter to cybercriminals.
SMEs are four times more likely to be hit by cyberattacks than large companies due to a lack of layers of protection . This leaves them vulnerable to data theft, fraud, and information leaks .
Hackers use bots to exploit vulnerabilities , regardless of company size. Small businesses without a dedicated IT team are even more exposed to automated attacks.
Furthermore, social engineering is a constant threat. Phony emails and fraudulent phone calls trick employees into stealing confidential information. Without regular security training , the risk increases considerably.
Small businesses are easy targets for hackers
Hackers know that small businesses often underinvest in digital security . Weak passwords , lack of updates, and lack of firewalls make them easy targets for ransomware and phishing .
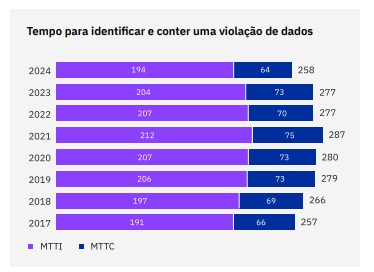
The absence of a security plan can have serious consequences . The average time to identify and contain breaches fell to 258 days in 2024 , the lowest in seven years, but still enough for sensitive data to be sold on the dark web , compromising customers and partners .
Small businesses think attacks are random , but hackers act strategically . Leaked credentials from major incidents are often used. Without two-factor authentication , a simple leak can lead to a complete system breach .
Examples of attacks on small businesses
Small businesses frequently face data theft and financial fraud . In 2021, Atento was the target of a cyberattack. Because its network was connected to its clients' banking systems, the attackers attempted to access these institutions. Although most banks were able to block the attempt, the company suffered losses of R$240 million , according to Infomoney.
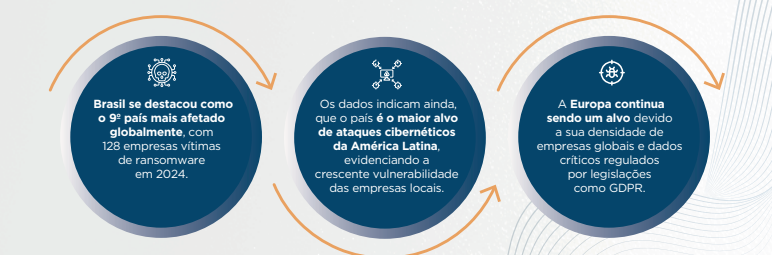
Ransomware is one of the biggest risks for small businesses. Hackers hijack data and demand a ransom, but many companies pay and never recover their information. In 2024, Brazil was the 9th most affected country , with 128 companies affected and an average cost of over R$7 million , according to an annual report by ISH .
phishing scams , where fraudulent emails trick employees into clicking on malicious links , giving them access to the company's network . In 2024, phishing accounted for 15% of attacks , but had the highest cost , reaching $4.88 million , according to IBM 's Cost of a Data Breach report .
How to protect yourself?
To reduce risks , it's essential to implement measures such as firewalls , DNS filtering , and two-factor authentication . Additionally, empowering employees to recognize threats can prevent attacks before they even occur .
Keeping systems up-to-date and performing frequent backups are essential. Companies that implement offline backups can recover data without having to pay ransoms to criminals . Furthermore, it's essential to restrict access to sensitive information to authorized employees only.
Finally, investing in digital security solutions that offer real-time protection can prevent attacks before they happen. The combination of a firewall, DNS filtering, and suspicious activity monitoring creates a solid barrier against cyberthreats.
Myth 2: “Antivirus is enough to guarantee security”
Antivirus is important, but not sufficient against modern threats like phishing and sophisticated malware . Many attacks bypass these basic protections. According to the Verizon Data Breach Report (2023) , 74% of breaches involved human factors , such as errors , social engineering , and stolen credentials .
Simply using antivirus software exposes your company to advanced attacks , such as social engineering and exploitation of unknown vulnerabilities . Many attacks go unnoticed until they cause significant damage .
Digital threats evolve rapidly , making antivirus signatures outdated . Relying solely on this solution increases the risk of attacks from newly developed malware . It's essential to adopt a layered security model for greater digital resilience .
Additional measures for digital protection
Digital security must include several complementary strategies to ensure a robust defense.
firewall
The firewall acts as a barrier between a company's internal network and external traffic , blocking unauthorized access. It is essential for preventing intrusions and attempts to exploit vulnerabilities.
DNS Filters
DNS filters block access to malicious websites , preventing employees from accidentally clicking on fraudulent links. This technology helps prevent phishing attacks and malware spread.
Two-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Using two-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification factor in addition to your password . This makes it harder for hackers to gain access, even if they manage to steal your login credentials.
Myth 3: “Complex passwords are secure enough”
While complex passwords are a good security measure, they aren't foolproof on their own. Studies indicate that 81% of data breaches are caused by weak or compromised passwords , revealing that a strong password, while important, isn't a guarantee of complete protection.
Furthermore, reusing passwords across platforms poses a significant risk . If a password is exposed in a data breach, all other accounts using the same password are vulnerable to attack . Therefore, adopting best practices such as using a password manager can help maintain unique and complex passwords for each service without the need to memorize them.
Additionally, enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) adds an extra layer of security by requiring a second verification method in addition to a password. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access, even if someone discovers the password.
It's equally important to review and change passwords periodically , especially after any security incident, to ensure compromised accounts are secured quickly.
The danger of reused passwords
Using reused passwords is a dangerous practice because it magnifies the impact of any data breach. When a password is exposed on one service, hackers can use it to attempt to access other accounts that use the same password, facilitating chain attacks.
One example of this is the use of leaked credentials to carry out "credential stuffing" , where hackers test these combinations across multiple websites and platforms . The impact of a single compromised password multiplies, compromising personal and corporate data. Therefore, never reusing passwords across different websites and services is one of the most effective ways to prevent vulnerability exploitation .
Good practices for secure passwords
To ensure password security, it's important to follow some best practices. First, each service should have a unique password , consisting of a combination of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters , ensuring complexity.
- Use a password manager – Using a password manager makes the process easier, allowing you to create and store strong, unique passwords without having to memorize them.
- Enable two-factor authentication (2FA) – Additionally, enabling two-factor authentication (2FA) should be a priority, as it requires a second form of verification, such as a code sent to your mobile phone, making it more difficult for attackers to access your account.
- Change passwords periodically, especially after breaches – Finally, changing passwords periodically, especially after data breaches, minimizes the risk of long-term exposure.
Myth 4: “Digital security is only the responsibility of the IT sector”
Digital security is a collective effort and cannot be delegated solely to the IT department. The fact is that cyberattacks often occur due to human error , and raising awareness among all employees is crucial to minimize these risks.
According to an IBM report , 22% of data breaches are caused by human error , such as clicking on malicious links or opening infected attachments. Therefore, everyone in the organization has a role to play in protecting data and systems, not just IT professionals.
Collaboration across different departments, coupled with well-established security practices, is crucial to creating a robust security culture within the company.
Digital security starts with every employee
Every employee is an important line of defense against cyberattacks. Advanced security systems are useless if employees aren't aware of the risks and best practices.
Security starts with simple actions, such as verifying the authenticity of received emails , avoiding using weak passwords, and not accessing sensitive data on public networks.
All team members should act as “first responders” in security matters, preparing to identify and mitigate threats before they become bigger problems.
How to involve the entire team in digital security?
Engaging the entire team in digital security requires ongoing training and clear policies regarding device and network usage.
Frequent training
Regular training should cover topics such as identifying phishing , best practices for creating passwords , and the safe use of digital platforms .

Clear internal policies on device and network usage
Additionally, clear internal policies, such as restrictions on the use of personal devices in the workplace and prohibiting access to unauthorized websites , should be implemented to ensure everyone follows secure procedures.
Open communication to report incidents quickly
Maintaining open communication and encouraging staff to quickly report any incidents or suspicious behavior is essential to acting quickly and preventing harm.
Myth 5: “Backups aren’t that important”
Backups are essential for data recovery in the event of catastrophic failures , such as ransomware attacks, hardware failures, or even natural disasters. Without adequate backups, companies can face irreparable damage, including loss of critical information and business interruption.
A NetApp report revealed that 20% of companies that lost data due to cyberattacks never fully recovered . Therefore, ensuring that your team performs regular and secure backups is one of the best ways to protect data integrity and maintain business continuity.
The importance of backup in data recovery
Backups are not just an "extra precaution," but a critical necessity for any organization. In ransomware attack scenarios, for example, the only form of safe recovery may be through backups, which avoid paying ransoms and protect against total data loss.
Creating backups shouldn't be done lightly ; you need to ensure that all important data, such as customer information and financial records, is included. Furthermore, these backups should be secured with encryption to prevent sensitive data from being exposed in the event of unauthorized access.
How to make a safe backup?
For secure backup, it's important to have a strategy that combines local and cloud backups.
- Cloud and local – Cloud backup offers advantages such as accessibility and protection against local disasters, while local backup can serve as an extra copy in case of network failures.
- Periodic backup updates – Additionally, backups should be updated periodically to ensure that the latest versions of the data are protected.
- Restore Testing – You should regularly perform restore tests on your backups to ensure they work properly and can be accessed quickly if needed.
Myth 6: “If I use a VPN, I’m 100% safe”
While VPNs (Virtual Private Networks) are valuable tools for protecting online privacy, they don't offer a complete solution for digital security . A VPN encrypts your internet connection and hides your location, which helps you access restricted content or protect data on public networks.
However, it's not a barrier against cyberthreats like phishing, malware, or social engineering . This is because, while a VPN can hide your identity and location, it doesn't prevent you from being tricked by fake links or downloading malicious files. Furthermore, many free VPNs don't offer the robust data protection needed to combat more sophisticated threats .
VPNs and their limits in digital security
VPNs are effective at encrypting data and protecting your privacy on unsecured networks, such as public Wi-Fi. However, they don't block malicious websites or protect against viruses or ransomware.
VPNs also don't offer effective defense against social engineering attacks, in which hackers manipulate victims into disclosing sensitive information. Therefore, VPNs are an important part of online security, but they shouldn't be seen as a complete solution. For more robust protection, other security measures must be implemented.
What else is needed besides VPN?
In addition to using a VPN, it's essential to adopt other digital security practices, such as firewalls, antivirus software, and malware protection systems. Implementing a DNS firewall, for example, can block malicious websites before they even reach you, providing an additional layer of defense.
Furthermore, it's crucial to have a real-time monitoring and alert system in place to detect any suspicious activity. Combining security tools like multi-factor authentication (MFA) and a regular software update policy strengthens defenses against a variety of cyberthreats.
This way, digital security becomes more comprehensive and vulnerabilities are minimized.
Myth 7: “My corporate email is secure because it’s in the cloud”
Many companies believe that their corporate emails are completely secure simply because they are hosted in the cloud, but this is a misconception.
While Google and Microsoft invest heavily in security to protect your data in cloud services, users also play an important role in corporate email security by managing it properly.
The risk of phishing attacks, for example, remains one of the biggest threats to businesses, regardless of where the email is hosted.
Check Point reports that currently over 90% of attacks on companies worldwide originate from malicious emails. Therefore, relying solely on cloud service security isn't enough to protect your corporate email.
The danger of phishing and credential leaks
Phishing continues to threaten corporate email security, especially when hackers target companies. Hackers often use spoofed emails to impersonate coworkers or vendors, requesting sensitive information such as login credentials or financial data .
Furthermore, credential leaks can occur in a variety of ways, whether through compromised websites or password reuse across multiple services. According to a Verizon security report , approximately 80% of phishing attacks target corporate emails, serving as a gateway for corporate network breaches.
Therefore, even if your email is in the cloud, it is essential that you implement additional measures to prevent these attacks.
How to protect your corporate email?
To ensure the protection of your corporate email, it's essential to adopt good security practices, such as implementing multi-factor authentication (MFA). MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide a second form of verification, such as an access code sent to their mobile phone.
Additionally, regular training on how to identify phishing emails and other threats is essential to reduce the risk of attack. Phishing detection tools, such as malicious email filters and suspicious link monitoring, also help protect employees from opening dangerous messages.
Keeping access credentials secure and never reusing them across different services is another fundamental step in protecting corporate email.
Conclusion: Protect your business by dispelling these myths
By debunking common beliefs about digital security, it becomes clear that online protection requires more than basic measures like using VPNs or relying solely on the cloud. True digital security requires a multifaceted approach, encompassing both robust technologies and educational practices.
Furthermore, collaboration across the team is essential to identify risks and respond quickly to incidents. Implementing complementary tools, such as firewalls, multi-factor authentication, and ongoing phishing training, is crucial to reducing vulnerabilities.
By adopting a proactive and comprehensive security strategy, your company can significantly reduce the risk of cyberattacks and ensure the protection of sensitive data against evolving threats.









